
The Anchorage
Personal website of Gregory K. Maxey, Commander USN (Retired)

The Anchorage
Personal website of Gregory K. Maxey, Commander USN (Retired)
The information, illustrations and code contained in my "Microsoft Word Tips" are provided free and without risk or obligation.


However, the work is mine. If you use it for commercial purposes or benefit from my efforts through income earned or time saved then a donation, however small, will help to ensure the continued availability of this resource.
If you would like to donate, please use the appropriate donate button to access PayPal. Thank you!
This Microsoft Word Tips & Microsoft Word Help page attempts to answer a frequently asked question from VBA enthusiast wanting to employ userforms: "How do I pass data from a calling VBA procedure to userform or vice versa.?""
If you are unfamiliar with userforms, see my: Create & Employ a Userform
The examples I will provide will illustrate a few of the various methods available. These examples illustrate both the calling procedure and userform code. You can download the demonstration document which includes the procedures and userforms used to create this tips page here: Userform Pass Data
The calling procedure for the this example is shown below:
Sub PassData1() Dim myFrm As UserForm1 Dim strCaption As String 'Get a dynamic value to be passed to the userform from the user. Do 'Define dynamic caption for userform frame control. strCaption = InputBox("Enter a custom Frame1 Caption: ", _ "Custom Caption", "Enter your shoe size e.g., 10D") 'Did the user cancel the inputbox? If StrPtr(strCaption) = 0 Then Exit Sub Loop Until strCaption <> "" 'Create\load the userform in memory. Set myFrm = New UserForm1 With myFrm 'Employ a direct reference a form built-in property. .Frame1.Caption = strCaption 'Display the form. .Show If .Tag <> "Canceled" Then 'Employ a direct reference to a form built-in property. MsgBox "You entered size " & UCase(.TextBox1.Text) & ". This" _ & " is a valid size.", , "Data Returned" End If End With Set myFrm = Nothing End Sub
This example uses a simple InputBox function to prompt the user for dynamic information to pass to the userform. This information is used to set caption text for a userform control.
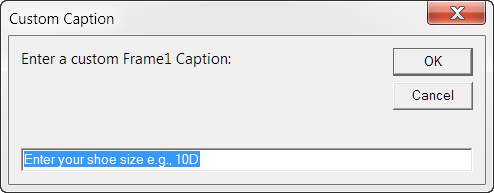
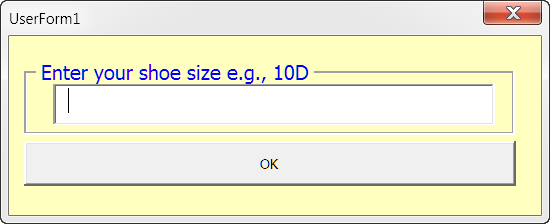
A direct reference to the form's .Frame1 control, built-in .Caption property is a simple method of passing data. As you can see below, the called userform displays caption text provided by the user in the calling procedure.
The code for the userform is provided below:
Private Sub cmdOK_Click()
If fcnSizeValidator(Me.TextBox1.Text) Then
Me.Hide
Else
With Me
.Frame1.Caption = Me.TextBox1.Text & " is invalid." _
& " Please enter a valid size."
With .TextBox1
.SetFocus
.SelStart = 0
.SelLength = Len(.Text)
End With
End With
End If
lbl_Exit:
Exit Sub
End Sub
Private Sub UserForm_QueryClose(Cancel As Integer, CloseMode As Integer)
'Intercept/repurpose Unload if user clicks form "X" close button.
If CloseMode = 0 Then
Cancel = True
Me.Tag = "Canceled"
Me.Hide
End If
lbl_Exit:
Exit Sub
End Sub
After the user enters a shoe size and clicks the userform "OK" command button, the userform cmdOK_Click procedure evaluates a valid data entry by passing the user entered data as as argument to a separate function procedure in a standard project module. The function procedure is shown below:
Function fcnSizeValidator(strSize As String) As Boolean
strSize = UCase(strSize)
Select Case True
Case Is = Val(Left(strSize, 2)) <= 16 _
And Val(Left(strSize, 2)) >= 2
Select Case True
Case Is = strSize Like "##[C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "#.#[C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "##.#[C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "##[C-E][C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "#.#[C-E][C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "##.#[C-E][C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "##[C-E][C-E][C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "#.#[C-E][C-E][C-E]" Or _
strSize Like "##.#[C-E][C-E][C-E]"
fcnSizeValidator = True
Case Else
fcnSizeValidator = False
End Select
Case Else
fcnSizeValidator = False
End Select
lbl_Exit:
Exit Function
End Function
When the user enters a valid size the cmdOK_Click procedure runs to termination and control is returned to the calling procedure.
In the calling procedure the data entered in the userform is returned using a simple VBA MsgBox function. Since the userform is still loaded in memory, its properties (i.e., .Textbox1.Text) can be evaluate directly in the calling procedure.
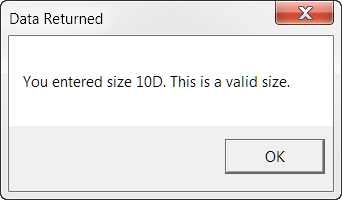
One of my early Senseis called this simple method the "Look Ma, no public variables method." There are no "Public" declared variables used to pass data to and from the calling procedure, the userform or other external processing procedures.
While simple, the method has a drawback. The drawback is that the form's controls are not encapsulated and are exposed to external procedures. For more on the importance of encapsulating userform code, see: UserForm – Advanced Notes & Tips.
You can encapsulate and avoid exposing your userform controls to external procedures by using one of the following four methods:
A userform displays data received from the calling macro and the interface to collect data for passing data back to the calling procedure.
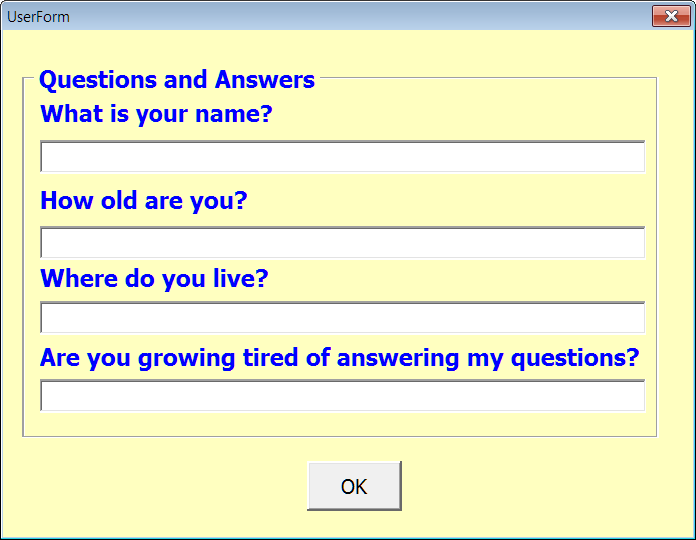
Again, the calling procedure uses a simple MsgBox function to display the data passed by the userform:
The code for the calling procedure and userform is provided below:
'Public data strings Public p_strCaptionLabel As String Public p_strAnswerReturned As String Sub PassData2() Dim myFrm As UserForm2 'Method 1 - Store the text to pass in a document variable. ActiveDocument.Variables("txtPassedToForm").Value = fcnCaptionText(2) 'Method 2 - Pass data to form using a public declared variable. p_strCaptionLabel = fcnCaptionText(1) 'Create/load instance of form. Set myFrm = New UserForm2 With myFrm 'Method 3 - Custom userform property w\publically declared data variables. myFrm.LabelCaption = fcnCaptionText(3) 'Method 4 - Custom userform property w\privately declared data variables. 'Pass (or Let) fcnCaptionText value to private form variable. .CaptionLabel = fcnCaptionText(4) .Show End With If Not myFrm.UserCancel Then 'Method 1. MsgBox "Answer 1: " _ & ActiveDocument.Variables("txtPassedToCall").Value, , "Text Returned" 'Method 2. MsgBox "Answer 2: " _ & p_strAnswerReturned, , "Text Returned" 'Method 3. MsgBox "Answer 3: " & myFrm.UserAnswer, , "Text Returned" 'Method 4. MsgBox "Answer 4: " & myFrm.Answer, , "Text Returned" End If lbl_Exit: Exit Sub End Sub Function fcnCaptionText(ByRef lngCount As Long) As String Select Case lngCount Case 1: fcnCaptionText = "What is your name?" Case 2: fcnCaptionText = "How old are you?" Case 3: fcnCaptionText = "Where do you live?" Case 4: fcnCaptionText = "Are you growing tired of answering my questions?" End Select lbl_Exit: Exit Function End Function
'Public form data variables. Public LabelCaption As String Public UserAnswer As String 'Private form data variables. Private m_strCaptionPassed As String Private m_strAnswerReturned As String Private m_Cancel As Boolean Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() 'This procedure is triggered when the form is loaded in memory. With Me 'Method 1. .Label1.Caption = ActiveDocument.Variables("txtPassedToForm").Value 'Method 2. .Label2.Caption = p_strCaptionLabel End With lbl_Exit: Exit Sub End Sub Private Sub UserForm_Activate() 'This procedure is triggered after the form loads and before it is shown to the user. With Me 'Method 3. .Label3.Caption = .LabelCaption 'Method 4. .Label4.Caption = .CaptionLabel End With lbl_Exit: Exit Sub End Sub Private Sub cmdOK_Click() With Me 'Method 1. If Len(.TextBox1.Text) > 0 Then ActiveDocument.Variables("txtPassedToCall").Value = .TextBox1.Text Else ActiveDocument.Variables("txtPassedToCall").Value = " " End If 'Method 2. p_strAnswerReturned = .TextBox2.Text 'Method 3. UserAnswer = .TextBox3.Text 'Method 4. m_strAnswerReturned = .TextBox4.Text .Hide End With lbl_Exit: Exit Sub End Sub Private Sub UserForm_QueryClose(Cancel As Integer, CloseMode As Integer) 'Intercept/repurpose Unload if user clicks form "X" close button. If CloseMode = 0 Then Cancel = True m_Cancel = True Me.Hide End If End Sub Public Property Let CaptionLabel(ByVal strDataLet As String) m_strCaptionPassed = strDataLet lbl_Exit: Exit Property End Property Public Property Get CaptionLabel() As String CaptionLabel = m_strCaptionPassed lbl_Exit: Exit Property End Property Public Property Get Answer() As String Answer = m_strAnswerReturned lbl_Exit: Exit Property End Property Public Property Get UserCancel() As Boolean UserCancel = m_Cancel lbl_Exit: Exit Property End Property
If you step through the procedures using the Visual Basic eiditor and the F8 key, it will help you see what is actually going on in the code.
Of the methods demonstrated, the last method is probably the most conventional. It is fully encapsulated and it employs private data variables in the userform class.
![]() See: Installing Macros for instructions on how to set up and use the macros provided in this Microsoft Word Help & Microsoft Word Tips page.
See: Installing Macros for instructions on how to set up and use the macros provided in this Microsoft Word Help & Microsoft Word Tips page.
![]() Note: This tips page, illustrations and examples were developed using Word 2003. It is wholly functional with Word 2007/2010.
Note: This tips page, illustrations and examples were developed using Word 2003. It is wholly functional with Word 2007/2010.
That's it! I hope you have found this tips page useful and informative.
The information, illustrations and code contained in my "Microsoft Word Tips" are provided free and without risk or obligation.


However, the work is mine. If you use it for commercial purposes or benefit from my efforts through income earned or time saved then a donation, however small, will help to ensure the continued availability of this resource.
If you would like to donate, please use the appropriate donate button to access PayPal. Thank you!